Summary and examples
A quadratic equation has the following general form:
![]()
It can be solved by factorization if the following conditions are satisfied:
 ,
, 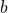 and
and  are whole numbers;
are whole numbers;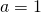 ;
;
if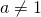 and left- and right-hand side are divided by
and left- and right-hand side are divided by  then the coefficients may not become fractions.
then the coefficients may not become fractions.
If this method does not work the ![]() formula has to be applied, see Quadratic equations (abc-formula).
formula has to be applied, see Quadratic equations (abc-formula).
The following examples will clarify this.
Example 1
Is factorizing useful in the following equations, and why (not)?
a. ![]()
Yes. ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() are whole numbers and
are whole numbers and ![]() .
.
b. ![]()
No. ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() are whole numbers. However,
are whole numbers. However, ![]() and dividing by
and dividing by ![]() gives fractions as coefficients.
gives fractions as coefficients.
c. ![]()
Yes. At first sight you might think 'no', because although ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() are whole numbers,
are whole numbers, ![]() . However, dividing by
. However, dividing by ![]() gives the resulting equation:
gives the resulting equation:
![]()
which satisfies the conditions. So finally 'yes'.
How do we use factorizing if we want to solve a quadratic equation? The following example will clarify this.
Try to write the equation:
![]()
in the form:
![]()
in which ![]() and
and ![]() are whole numbers.
are whole numbers.
We have to determine ![]() and
and ![]() such that the equation:
such that the equation:
![]()
is equal to the equation:
![]()
This is the case if ![]() and
and ![]() satisfy the following equations:
satisfy the following equations:
![]()
and:
![]()
So find two numbers ![]() and
and ![]() of which the product equals
of which the product equals ![]() and their sum equals
and their sum equals ![]() . We find
. We find ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
The equation can thus be written as:
![]()
or:
![]()
We have to solve the equation:
![]()
or:
![]() or
or ![]()
The solution is:
![]() or
or ![]()
This method is to be preferred when you have enough skills. However, the method is not always applicable and then the ![]() -formule has to be applied.
-formule has to be applied.
Example 2
Solve:
![]()
We have to find ![]() and
and ![]() such that:
such that:
![]() and
and ![]()
The following values satisfy:
![]() and
and ![]()
and thus the equation can be written as:
![]()
The solutions are:
![]() or
or ![]()
Example 3
Solve:
![]()
We have to find ![]() and
and ![]() such that:
such that:
![]() and
and ![]()
The following values satisfy:
![]() and
and ![]()
Thus the equation can be written as:
![]()
with the following solutions:
![]() or
or ![]()
Example 4
Solve:
![]()
We have to find ![]() and
and ![]() such that:
such that:
![]() and
and ![]()
The following values satisfy:
![]() and
and ![]()
Thus the equation can be written as:
![]()
The solutions are:
![]() or
or ![]()
Example 5
Solve:
![]()
We have to find ![]() and
and ![]() such that:
such that:
![]() and
and ![]()
The following values satisfy:
![]() and
and ![]()
Thus the equation can be written as:
![]()
The solutions are:
![]() or
or ![]()
Example 6
Solve:
![]()
We have to find ![]() and
and ![]() such that:
such that:
![]() and
and ![]()
There are no whole numbers ![]() and
and ![]() which satisfy these conditions. This does not mean that the quadratic equation has no solutions. In this case it appears that the equation do have solutions and we can find them by applying the
which satisfy these conditions. This does not mean that the quadratic equation has no solutions. In this case it appears that the equation do have solutions and we can find them by applying the ![]() -formula, see Quadratic equations (abc-formula).
-formula, see Quadratic equations (abc-formula).
Example 7
Solve:
![]()
We have to find ![]() and
and ![]() such that:
such that:
![]() and
and ![]()
There are no whole numbers ![]() and
and ![]() which satisfy these conditions. This does not mean that the quadratic equation has no solutions. However, in this case it appears that the equation has no solutions, because the discriminant of the equation is negative and then the equation does not have real solutions, see also Quadratic equations (abc-formula).
which satisfy these conditions. This does not mean that the quadratic equation has no solutions. However, in this case it appears that the equation has no solutions, because the discriminant of the equation is negative and then the equation does not have real solutions, see also Quadratic equations (abc-formula).

